Nitrous oxide
| Nitrous oxide | |
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
|
Dinitrogen monoxide
|
|
|
Other names
Laughing gas
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 10024-97-2 |
| PubChem | 948 |
| ChemSpider | 923 |
| UN number | 1070 (compressed) 2201 (liquid) |
| ChEBI | 17045 |
| RTECS number | QX1350000 |
| ATC code | N01 |
|
InChI
InChI=InChI=1/N2O/c1-2-3
|
|
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | N2O |
| Molar mass | 44.013 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| Density | 1.977 g/L (gas) |
| Melting point |
–90.86 °C (182.29 K) |
| Boiling point |
–88.48 °C (184.67 K) |
| Solubility in water | 0.15 g/100 ml (15 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, ether, sulfuric acid |
| log P | 0.35 |
| Vapor pressure | 5150 kPa (20 °C) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.330 |
| Structure | |
| Molecular shape | linear, C∞v |
| Dipole moment | 0.166 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
+82.05 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
219.96 J K–1 mol–1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Routes of administration |
Inhalation |
| Metabolism | 0.004% |
| Elimination half-life |
5 minutes |
| Excretion | Respiratory |
| Pregnancy category |
C(US) |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | Ilo.org, ICSC 0067 |
| EU Index | Oxidant [O] |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
2
0
OX
|
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Related nitrogen oxides | Nitric oxide Dinitrogen trioxide Nitrogen dioxide Dinitrogen tetroxide Dinitrogen pentoxide |
| Related compounds | Ammonium nitrate Azide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
|
| Infobox references | |
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas, is a chemical compound with the formula N2O. It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic effects. It is known as "laughing gas" due to the euphoric effects of inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative hallucinogen. It is also used as an oxidizer in rocketry and in motor racing to increase the power output of engines. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidizer similar to molecular oxygen.
Nitrous oxide gives rise to NO on reaction with oxygen atoms, and this NO in turn reacts with ozone. As a result, it is the main naturally occurring regulator of stratospheric ozone. It is also a major greenhouse gas and air pollutant. Considered over a 100 year period, it has 298 times more impact per unit weight than carbon dioxide.[1]
Contents |
History
The gas was first synthesized by English natural philosopher and chemist Joseph Priestley in 1772, who called it phlogisticated nitrous air (see phlogiston).[2] Priestley published his discovery in the book Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air (1775), where he described how to produce the preparation of "nitrous air diminished", by heating iron filings dampened with nitric acid.[3]
Early use (1794-1843)
First important use of nitrous oxide, was made possible by Thomas Beddoes and the renowned engineer James Watt, who worked together to publish the book Considerations on the Medical Use and on the Production of Factitious Airs (1794). This book was important for two reasons. First, James Watt had invented a novel machine to produce "Factitious Airs" (i.e. nitrous oxide) and a novel "breathing apparatus" to inhale the gas. Second, the book also presented the new medical theories by Thomas Beddoes, that tuberculosis and other lung diseases could be treated by inhalation of "Factitious Airs".[4]
The machine to produce "Factitious Airs" comprised three parts: A furnace to burn the needed material, a vessel with water where the produced gas passed through in a spiral pipe (in order for impurities to be "washed off"), and finally the gas cylinder with a gasometer where the produced air could be tapped into portable air bags (made of airtight oily silk). The breathing apparatus comprised one of the portable air bags connected with a tube to a mouthpiece. With this new equipment being engineered and produced already in 1794, the way was now paved for clinical trials, which began when Thomas Beddoes in 1798 established the "Pneumatic Institution for Relieving Diseases by Medical Airs" in Clifton (Bristol). In the basement of the building, a large scale machine was producing the gases under the supervision of a young Humphry Davy, who was encouraged to experiment with new gases for patients to inhale.[4] The first important work of Davy was to examine the nitrous oxide, with the results being published in his book: Researches, Chemical and Philosophical (1800). In that publication, Davy notes the analgesic effect of nitrous oxide at page 465 and its potential to be used for surgical operations at page 556.[5]
Despite the valuable finding made by Davy, that inhalation of nitrous oxide could relieve a conscious person from pain, another 44 years would elapse before doctors attempted to use it for anaesthesia. The use of nitrous oxide as a recreational drug at "laughing gas parties", primarily arranged for the British upper class, became an immediate success beginning in 1799. While the effects of the gas generally make the user feel stuporous, dreamy and sedated, some people also "get the giggles" in a state of euphoria, and erupt in laughter and overall amusement.[6]
Anesthetic use
The first time nitrous oxide was used as anesthetic drug in the treatment of a patient, was when dentist Horace Wells with assistance by Gardner Quincy Colton and John Mankey Riggs, demonstrated insensitivity to pain from a dental extraction in December 1844.[7] In the following weeks, Wells treated the first 12-15 patients with nitrous oxide in Hartford, and according to his own record only failed in two cases.[8] In spite of these convincing results being reported by Wells to the medical society in Boston already in December 1844, this new method was not immediately adopted by other dentists. The reason for this was most likely, that Wells in January 1845 at his first public demonstration towards the medical faculty in Boston, had been partly unsuccessful, leaving his colleagues doubtful regarding its efficacy and safety.[9] The method did not come into general use until 1863, when Gardner Quincy Colton successfully started to use it in all his "Colton Dental Association" clinics, that he just had established in New Haven and New York City.[4] Over the following three years, Colton and his associates successfully administered nitrous oxide to more than 25,000 patients.[10] With its efficacy and safety now demonstrated by large numbers, the usage of nitrous oxide rapidly became the preferred anesthetic method in dentistry. Because the gas is mild enough to keep a patient in a conscious and conversational state, and yet in most cases strong enough to suppress the pain caused by dental work, it remains the preferred gas anesthetic in today's dentistry.
In hospitals, nitrous oxide was however found not to be a strong enough anesthetic for the use in large operations. Being a stronger and more potent anesthetic, sulfuric ether was instead demonstrated and accepted for use in October 1846, along with chloroform in 1847.[4] When Joseph Thomas Clover invented the "gas-ether inhaler" in 1876, it however became a common practice at hospitals to initiate all anesthetic treatments with a mild flow of nitrous oxide, and then gradually increase the anaesthesia with the stronger ether/chloroform. Clover's gas-ether inhaler was designed to supply the patient with nitrous oxide and ether at the same time, with the exact mixture being controlled by the operator of the device. It remained in use by many hospitals until the 1930s.[10] Although hospitals today are using a more advanced anaesthetic machine, these machines still use the same principle launched with Clover's gas-ether inhaler: To initiate the anesthesia with nitrous oxide, before the administration of a more powerful anesthetic.
Production
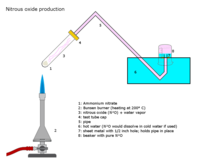
Nitrous oxide is most commonly prepared by careful heating of ammonium nitrate, which decomposes into nitrous oxide and water vapor.[11] The addition of various phosphates favors formation of a purer gas at slightly lower temperatures. One of the earliest commercial producers was George Poe in Trenton, New Jersey.[12]
- NH4NO3 (s) → 2 H2O (g) + N2O (g)
This reaction occurs between 170 and 240 °C, temperatures where ammonium nitrate is a moderately sensitive explosive and a very powerful oxidizer. Above 240 °C the exothermic reaction may accelerate to the point of detonation, so the mixture must be cooled to avoid such a disaster. Superheated steam is used to reach reaction temperature in some turnkey production plants.[13]
Downstream, the hot, corrosive mixture of gases must be cooled to condense the steam, and filtered to remove higher oxides of nitrogen. Ammonium nitrate smoke, as an extremely persistent colloid, will also have to be removed. The cleanup is often done in a train of 3 gas washes; namely base, acid and base again. Any significant amounts of nitric oxide (NO) may not necessarily be absorbed directly by the base (sodium hydroxide) washes.
The nitric oxide impurity is sometimes chelated out with ferrous sulfate, reduced with iron metal, or oxidised and absorbed in base as a higher oxide. The first base wash may (or may not) react out much of the ammonium nitrate smoke. However, this reaction generates ammonia gas, which may have to be absorbed in the acid wash.
Other routes
The direct oxidation of ammonia may someday rival the ammonium nitrate pyrolysis synthesis of nitrous oxide mentioned above. This capital-intensive process, which originates in Japan, uses a manganese dioxide-bismuth oxide catalyst:[14]
- 2 NH3 + 2 O2 → N2O + 3 H2O
Higher oxides of nitrogen are formed as impurities. In comparison, uncatalyzed ammonia oxidation (i.e. combustion or explosion) goes primarily to N2 and H2O.
Nitrous oxide can be made by heating a solution of sulfamic acid and nitric acid. Many gases are made this way in Bulgaria.[15]
- HNO3 + NH2SO3H → N2O + H2SO4 + H2O
There is no explosive hazard in this reaction if the mixing rate is controlled. However, as usual, toxic higher oxides of nitrogen are formed.
Nitrous oxide is produced in large volumes as a by-product in the synthesis of adipic acid; one of the two reactants used in nylon manufacture.[16][17] This might become a major commercial source, but will require the removal of higher oxides of nitrogen and organic impurities. Currently much of the gas is decomposed before release for environmental protection. Greener processes may prevail that substitute hydrogen peroxide for nitric acid oxidation; hence no generation of oxide of nitrogen by-products.
Hydroxylammonium chloride can react with sodium nitrite to produce N2O as well:
- NH3OH+Cl− + NaNO2 → N2O + NaCl + 2 H2O
If the nitrite is added to the hydroxylamine solution, the only remaining byproduct is salt water. However, if the hydroxylamine solution is added to the nitrite solution (nitrite is in excess), then toxic higher oxides of nitrogen are also formed. Also, HNO3 can be reduced to N2O by SnCl2 and HCl mixture:
- 2 HNO3 + 8 HCl + 4 SnCl2 → 5 H2O + 4 SnCl4 + N2O
Applications
Rocket motors
Nitrous oxide can be used as an oxidizer in a rocket motor. This has the advantages over other oxidizers in that it is non-toxic and, due to its stability at room temperature, easy to store and relatively safe to carry on a flight. As a secondary benefit it can be readily decomposed to form breathing air. Its high density and low storage pressure enable it to be highly competitive with stored high-pressure gas systems.
In a 1914 patent, American rocket pioneer Robert Goddard suggested nitrous oxide and gasoline as possible propellants for a liquid-fueled rocket. Nitrous oxide has been the oxidizer of choice in several hybrid rocket designs (using solid fuel with a liquid or gaseous oxidizer). The combination of nitrous oxide with hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene fuel has been used by SpaceShipOne and others. It is also notably used in amateur and high power rocketry with various plastics as the fuel.
Nitrous oxide can also be used in a monopropellant rocket. In the presence of a heated catalyst, N2O will decompose exothermically into nitrogen and oxygen, at a temperature of approximately 1300 °C. Because of the large heat release, the catalytic action rapidly becomes secondary as thermal autodecomposition becomes dominant. In a vacuum thruster, this can provide a monopropellant specific impulse (Isp) of as much as 180 s. While noticeably less than the Isp available from hydrazine thrusters (monopropellant or bipropellant with nitrogen tetroxide), the decreased toxicity makes nitrous oxide an option worth investigating.
Specific impulse (Isp) can be improved by blending a hydrocarbon fuel with the nitrous oxide inside the same storage tank, becoming a nitrous oxide fuel blend (NOFB) monopropellant. This storage mixture does not incur the danger of spontaneous ignition, since N2O is chemically stable. When the nitrous oxide decomposes by a heated catalyst, high temperature oxygen is released and rapidly ignites the hydrocarbon fuel-blend. NOFB monopropellants are capable of Isp greater than 300 seconds, while avoiding the toxicity associated with hypergolic propulsion systems.[18][19] The low freezing point of NOFB eases thermal management compared to hydrazine and dinitrogen tetroxide—a valuable property for space storable propellants.
Internal combustion engine
In vehicle racing, nitrous oxide (often referred to as just "nitrous") allows the engine to burn more fuel and air, resulting in a more powerful combustion. The gas itself is not flammable, but it delivers more oxygen than atmospheric air by breaking down at elevated temperatures.
Nitrous oxide is stored as a compressed liquid; the evaporation and expansion of liquid nitrous oxide in the intake manifold causes a large drop in intake charge temperature, resulting in a denser charge, further allowing more air/fuel mixture to enter the cylinder. Nitrous oxide is sometimes injected into (or prior to) the intake manifold, whereas other systems directly inject right before the cylinder (direct port injection) to increase power.
The technique was used during World War II by Luftwaffe aircraft with the GM-1 system to boost the power output of aircraft engines. Originally meant to provide the Luftwaffe standard aircraft with superior high-altitude performance, technological considerations limited its use to extremely high altitudes. Accordingly, it was only used by specialized planes like high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft, high-speed bombers, and high-altitude interceptor aircraft.
One of the major problems of using nitrous oxide in a reciprocating engine is that it can produce enough power to damage or destroy the engine. Very large power increases are possible, and if the mechanical structure of the engine is not properly reinforced, the engine may be severely damaged or destroyed during this kind of operation. It is very important with nitrous oxide augmentation of internal combustion engines to maintain proper operating temperatures and fuel levels to prevent "preignition", or "detonation" (sometimes referred to as "knocking" or "pinging"). Most problems that are associated with nitrous do not come from mechanical failure due to the power increases. Since nitrous allows a much denser charge into the cylinder it dramatically increases cylinder pressures. The increased pressure and temperature can cause problems such as melting the piston or valves. It may also crack or warp the piston or head and cause preignition due to uneven heating.
Automotive-grade liquid nitrous oxide differs slightly from medical-grade nitrous oxide. A small amount of sulfur dioxide is added to prevent substance abuse.[20]
Aerosol propellant

The gas is approved for use as a food additive (also known as E942), specifically as an aerosol spray propellant. Its most common uses in this context are in aerosol whipped cream canisters, cooking sprays, and as an inert gas used to displace oxygen, to inhibit bacterial growth, when filling packages of potato chips and other similar snack foods.
The gas is extremely soluble in fatty compounds. In aerosol whipped cream, it is dissolved in the fatty cream until it leaves the can, when it becomes gaseous and thus creates foam. Used in this way, it produces whipped cream four times the volume of the liquid, whereas whipping air into cream only produces twice the volume. If air were used as a propellant, oxygen would accelerate rancidification of the butterfat; nitrous oxide inhibits such degradation. Carbon dioxide cannot be used for whipped cream because it is acidic in water, which would curdle the cream and give it a seltzer-like 'sparkling' sensation.
However, the whipped cream produced with nitrous oxide is unstable and will return to a more or less liquid state within half an hour to one hour. Thus, the method is not suitable for decorating food that will not be immediately served.
Similarly, cooking spray, which is made from various types of oils combined with lecithin (an emulsifier), may use nitrous oxide as a propellant; other propellants used in cooking spray include food-grade alcohol and propane.
Users of nitrous oxide often obtain it from whipped cream dispensers that use nitrous oxide as a propellant (see above section), for recreational use as a euphoria-inducing inhalant drug. It is not harmful in small doses, but risks due to lack of oxygen do exist (see Recreational use below).
In medicine

Nitrous oxide has been used for anesthesia in dentistry since December 1844, where Horace Wells made the first 12-15 dental operations with the gas in Hartford. Its debut as a generally accepted method however only came in 1863, when Gardner Quincy Colton introduced it more broadly at all the Colton Dental Association clinics, that he founded in New Haven and New York city.[4] The first devices used in dentistry to administer the gas, known as Nitrous Oxide inhalers, were designed in a very simple way with the gas stored and breathed through a breathing bag made of rubber cloth, without a scavenger system and flowmeter, and with no addition of oxygen/air.[10] Today these simple and somewhat unreliable inhalers, of course have been replaced by the more modern relative analgesia machine, which is an automated machine designed to deliver a precisely dosed and breath-actuated flow of nitrous oxide mixed with oxygen, for the patient to inhale safely. The machine used in dentistry is designed as a more simplified version of the larger anaesthetic machine used by hospitals, as it doesn't feature the additional anaesthetic vaporiser and medical ventilator. The purpose of the machine allows for a more simple design, as it only delivers a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen for the patient to inhale, in order to depress the feeling of pain -while keeping the patient in a conscious state.
The relative analgesia machine typically feature a constant-supply flowmeter, which allow the proportion of nitrous oxide and the combined gas flow rate to be individually adjusted. The gas is administered by dentists through a demand-valve inhaler over the nose, which will only release gas when the patient inhales through the nose. Because nitrous oxide is minimally metabolized in humans (with a rate of 0.004%), it retains its potency when exhaled into the room by the patient, and can pose an intoxicating and prolonged exposure hazard to the clinic staff if the room is poorly ventilated. Where nitrous oxide is administered, a continuous-flow fresh-air ventilation system or nitrous scavenger system is used to prevent a waste-gas buildup.
Hospitals are administering nitrous oxide as one of the anesthetic drugs delivered by anaesthetic machines. Nitrous oxide is a weak general anesthetic, and so is generally not used alone in general anesthesia. In general anesthesia it is used as a carrier gas in a 2:1 ratio with oxygen for more powerful general anesthetic drugs such as sevoflurane or desflurane. It has a MAC (minimum alveolar concentration) of 105% and a blood:gas partition coefficient of 0.46.
When nitrous oxide is inhaled as the only anesthetic drug, it is normally administered as a mixture with 30% gas and 70% oxygen.[21] The medical grade gas tanks, with the tradename Entonox and Nitronox contain a mixture with 50%, but this will normally be diluted to a lower percentage upon the operational dilevery to the patient. Inhalation of nitrous oxide is frequently used to relieve pain associated with childbirth, trauma, oral surgery, and heart attacks.
In Britain, Entonox and Nitronox are commonly used by ambulance crews (including unregistered practitioners) as a rapid and highly effective analgesic gas.
Recreational use
Nitrous oxide can cause analgesia, depersonalization, derealization, dizziness, euphoria, and some sound distortion.[22] Research has also found that it increases suggestibility and imagination.[23] Inhalation of nitrous oxide for recreational use, with the purpose to cause euphoria and slight hallucinations, began as a phenomenon for the British upper class in 1799, known as "laughing gas parties". Until at least 1863, a low availability of equipment to produce the gas, combined with a low usage of the gas for medical purposes, meant it was a relatively rare phenomenon that mainly took place among students at medical universities. When equipment became more widely available for dentistry and hospitals, most countries also restricted the legal access to buy pure nitrous oxide gas cylinders to those sectors. As only medical staff and dentists today are legally allowed to buy the pure gas, the recreational use is also believed to be somewhat limited. The consumers union report from 1972, however found that the use of the gas for recreational purpose still take place in present time, based upon reports of its use in Maryland 1971, Vancouver 1972, and a survey made by Dr.Edward J.Lynn of its nonmedical use in Michigan 1970.[6]
- Citation of the results from the Michigan survey in 1970: "It was not uncommon [in the interviews] to hear from individuals who had been to parties where a professional (doctor, nurse, scientist, inhalation therapist, researcher) had provided nitrous oxide. There also were those who work in restaurants who used the N2O stored in tanks for the preparation of whip cream. Reports were received from individuals who used the gas contained in aerosol cans both of food and non-food products. At a recent rock festival nitrous oxide was widely sold for 25 cents a balloon. Contact was made with a "mystical-religious" group that used the gas to accelerate arriving at their transcendental-meditative state of choice. Although a few, more sophisticated users employed nitrous oxide-oxygen mixes with elaborate equipment, most users employed balloons or plastic bags. They either held a breath of N2O or rebreathed the gas. There were no adverse effects reported in the more than one hundred individuals surveyed." [6]
Inhaling nitrous oxide from tanks used in automotive systems is unsafe, because the toxic gas sulfur dioxide is mixed in around 100 ppm, specifically to discourage recreational use.[20]
Neuropharmacology
The pharmacological mechanism of action of N2O in medicine is not fully known. However, it has been shown to directly modulate a broad range of ligand-gated ion channels, and this likely plays a major role in many of its effects. It moderately blocks NMDA and β2-subunit-containing nACh channels, weakly inhibits AMPA, kainate, GABAC, and 5-HT3 receptors, and slightly potentiates GABAA and glycine receptors.[24][25] It has also been shown to activate two-pore-domain K+ channels.[26] While N2O affects quite a few ion channels, its anesthetic, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant effects are likely caused predominantly or fully via inhibition of NMDAR-mediated currents.[24][27] In addition to its effects on ion channels, N2O may act to imitate nitric oxide (NO) in the central nervous system as well, and this may relate to its analgesic and anxiolytic properties.[27]
Anxiolytic effect
In behavioral tests of anxiety, a low dose of N2O is an effective anxiolytic, and this anti-anxiety effect is associated with enhanced activity of GABAA receptors as it is partially reversed by benzodiazepine receptor antagonists. Mirroring this, animals which have developed tolerance to the anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines are partially tolerant to N2O.[28] Indeed, in humans given 30% N2O, benzodiazepine receptor antagonists reduced the subjective reports of feeling "high", but did not alter psycho-motor performance, in human clinical studies.[29]
Analgesic effect
The analgesic effects of N2O are linked to the interaction between the endogenous opioid system and the descending noradrenergic system. When animals are given morphine chronically they develop tolerance to its pain-killing effects, and this also renders the animals tolerant to the analgesic effects of N2O.[30] Administration of antibodies which bind and block the activity of some endogenous opioids (not β-endorphin) also block the antinociceptive effects of N2O.[31] Drugs which inhibit the breakdown of endogenous opioids also potentiate the antinociceptive effects of N2O.[31] Several experiments have shown that opioid receptor antagonists applied directly to the brain block the antinociceptive effects of N2O, but these drugs have no effect when injected into the spinal cord.
Conversely, α2-adrenoceptor antagonists block the antinociceptive effects of N2O when given directly to the spinal cord, but not when applied directly to the brain.[32] Indeed, α2B-adrenoceptor knockout mice or animals depleted in norepinephrine are nearly completely resistant to the antinociceptive effects of N2O.[33] It seems N2O-induced release of endogenous opioids causes disinhibition of brain stem noradrenergic neurons, which release norepinephrine into the spinal cord and inhibit pain signaling.[34] Exactly how N2O causes the release of endogenous opioid peptides is still uncertain.
Euphoric effect
In rats, N2O stimulates the mesolimbic reward pathway via inducing dopamine release and activating dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens, presumably through antagonization of NMDA receptors localized in the system.[35][36][37][38] This action has been implicated in its euphoric effects, and notably, appears to augment its analgesic properties as well.[35][36][37][38]
However, it is remarkable that in mice, N2O blocks amphetamine-induced and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and behavioral sensitization, abolishes the conditioned place preference (CPP) of cocaine and morphine, and does not produce reinforcing (or aversive) effects of its own.[39][40] Studies on CPP of N2O in rats is mixed, consisting of reinforcement, aversion, and no change.[41] In contrast, it is a positive reinforcer in squirrel monkeys,[42] and is well known as a drug of abuse in humans.[43] These discrepancies in response to N2O may reflect specie variations or methodological differences.[40] Though, it is noteworthy that in human clinical studies, N2O was found to produce mixed responses similarly to rats, reflecting high subjective individual variability.[44][45]
Neurotoxicity
Similarly to other NMDA antagonists like ketamine, N2O has been demonstrated to produce neurotoxicity in the form of Olney's lesions (damage to the posterior cingulate and retrosplenial cortices of the brain) in rodents upon prolonged (e.g., several hour) exposure.[46][47][48][49] However, it also simultaneously exerts widespread neuroprotective effects via inhibiting glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, and it has been argued that on account of its very short duration under normal circumstances, N2O may not share the neurotoxicity of other NMDA antagonists.[50] Indeed, in rodents, short-term exposure results in only mild injury that is rapidly reversible, and permanent neuronal death only occurs after constant and sustained exposure.[46]
Safety
The major safety hazards of nitrous oxide come from the fact that it is a compressed liquefied gas, an asphyxiation risk, and a dissociative anaesthetic. Exposure to nitrous oxide causes short-term decreases in mental performance, audiovisual ability, and manual dexterity.[51] Long term exposure can cause vitamin B12 deficiency, numbness, reproductive side effects, and other problems (see Recreational use and Biological factors in this article).
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health recommends that workers' exposure to nitrous oxide should be controlled during the administration of anesthetic gas in medical, dental, and veterinary operators.[52]
Chemical/physical
At room temperature (20°C) the saturated vapor pressure is 58.5 bar, rising up to 72.45 bar at 36.4°C — the critical temperature. The pressure curve is thus unusually sensitive to temperature.[53] Liquid nitrous oxide acts as a good solvent for many organic compounds; liquid mixtures may form shock sensitive explosives.
As with many strong oxidizers, contamination of parts with fuels have been implicated in rocketry accidents, where small quantities of nitrous/fuel mixtures explode due to 'water hammer' like effects (sometimes called 'dieseling' — heating due to adiabatic compression of gases can reach decomposition temperatures).[54] Some common building materials such as stainless steel and aluminium can act as fuels with strong oxidisers such as nitrous oxide, as can contaminants, which can ignite due to adiabatic compression.[55]
There have also been accidents where nitrous oxide decomposition in plumbing has led to the explosion of large tanks.[56]
Biological
Nitrous oxide inactivates the cobalamin form of vitamin B12 by oxidation. Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency, including sensory neuropathy, myelopathy, and encephalopathy, can occur within days or weeks of exposure to nitrous oxide anesthesia in people with subclinical vitamin B12 deficiency. Symptoms are treated with high doses of vitamin B12, but recovery can be slow and incomplete.[57] People with normal vitamin B12 levels have stores to make the effects of nitrous oxide insignificant, unless exposure is repeated and prolonged (nitrous oxide abuse). Vitamin B12 levels should be checked in people with risk factors for vitamin B12 deficiency prior to using nitrous oxide anesthesia.
A study of workers[58] and several experimental animal studies[59][59][60][61] indicate that adverse reproductive effects for pregnant females may also result from chronic exposure to nitrous oxide.
Environmental
Nitrous oxide is a greenhouse gas, accounting for around 6% of the heating effect of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.[62] According to 2006 data from the United States Environmental Protection Agency, industrial sources make up only about 20% of all anthropogenic sources, and include the production of nylon, and the burning of fossil fuel in internal combustion engines. Human activity is thought to account for 30%; tropical soils and oceanic release account for 70%.[63] However, a 2008 study by Nobel Laureatte Paul Crutzen suggests that the amount of nitrous oxide release attributable to agricultural nitrate fertilizers has been seriously underestimated, most of which would presumably come under soil and oceanic release in the Environmental Protection Agency data.[64] Atmospheric levels have risen by more than 15% since 1750.[65] Nitrous oxide also causes ozone depletion. A new study suggests that N2O emission currently is the single most important ozone-depleting substance (ODS) emission and is expected to remain the largest throughout the 21st century.[66][67]
Legality
In the United States, possession of nitrous oxide is legal under federal law and is not subject to DEA purview.[68] It is, however, regulated by the Food and Drug Administration under the Food Drug and Cosmetics Act; prosecution is possible under its "misbranding" clauses, prohibiting the sale or distribution of nitrous oxide for the purpose of human consumption.
Many states have laws regulating the possession, sale, and distribution of nitrous oxide. Such laws usually ban distribution to minors or limit the amount of nitrous oxide that may be sold without special license.
- In the state of California, possession for recreational use is prohibited and qualifies as a misdemeanor.[69]
In some countries, it is illegal to have nitrous oxide systems plumbed into an engine's intake manifold. These laws are ostensibly used to prevent street racing and to meet emission standards.
Nitrous oxide is entirely legal to possess and inhale in the United Kingdom, although supplying it to others to inhale, especially minors, is more likely to end up with a prosecution under the Medicines Act.
In New Zealand, the Ministry of Health has warned that nitrous oxide is a prescription medicine, and its sale or possession without a prescription is an offense under the Medicines Act.[70] This statement would seemingly prohibit all non-medicinal uses of the chemical, though it is implied that only recreational use will be legally targeted.
In India, for general anaesthesia purposes, nitrous oxide is available as Nitrous Oxide IP. India's gas cylinder rules (1985) permit the transfer of gas from one cylinder to another for breathing purposes. This law benefits remote hospitals, which would otherwise suffer as a result of India's geographic immensity. Nitrous Oxide IP is transferred from bulk cylinders (17,000 liters capacity gas) to smaller pin-indexed valve cylinders (1,800 liters of gas), which are then connected to the yoke assembly of Boyle's machines. Because India's Food & Drug Authority (FDA-India) rules state that transferring a drug from one container to another (refilling) is equivalent to manufacturing, anyone found doing so must possess a drug manufacturing license.
See also
- Whipped-cream charger
- Diffusion hypoxia
References
- ↑ 2007 IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) by Working Group 1 (WG1), Chapter 2 "Changes in Atmospheric Constituents and in Radiative Forcing" which contains information on global warming potential (GWP) of greenhouse gases.
- ↑ Keys TE (1941). "The_Development_of_Anesthesia". Anesthesiology journal 2: 552–574. http://journals.lww.com/anesthesiology/citation/1941/09000/The_Development_of_Anesthesia.8.aspx.
- ↑ Priestley J (1776). "Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air (vol.2, sec.3)". http://www.erowid.org/chemicals/nitrous/nitrous_journal1.shtml.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Sneader W (2005). Drug Discovery –A History. John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 9780471899808. http://books.google.com/?id=mYQxRY9umjcC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Drug+Discovery+history&cd=1. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ↑ Davy H (1800). Researches, chemical and philosophical –chiefly concerning nitrous oxide or dephlogisticated nitrous air, and its respiration. Printed for J. Johnson. http://books.google.com/?id=jhUAAAAAQAAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=Researches,+chemical+and+philosophical&cd=1#v=onepage&q.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Brecher EM (1972). "Consumers Union Report on Licit and Illicit Drugs, Part VI - Inhalants and Solvents and Glue-Sniffing". Consumer Reports Magazine. http://www.druglibrary.org/schaffer/Library/studies/cu/CU43.html.
- ↑ Erving HW (1933). "The Discoverer of Anæsthesia: Dr. Horace Wells of Hartford". Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine, May 1933; v.5, n.5, p.421–430. http://ukpmc.ac.uk/picrender.cgi?artid=1703729&blobtype=pdf.
- ↑ Wells H (1847). A history of the discovery, of the application of nitrous oxide gas, ether, and other vapors, to surgical operations. J. Gaylord Wells. http://books.google.com/?id=exNtlBi8T4EC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Horace+Wells#v=onepage&q.
- ↑ Desai SP, Desai MS, Pandav CS (2007). "The discovery of modern anaesthesia-contributions of Davy, Clarke, Long, Wells and Morton". Indian J Anaesth 2007;51:472-8. http://www.ijaweb.org/text.asp?2007/51/6/472/61183.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Miller AH (1941). "Technical Development of Gas Anesthesia". Anesthesiology journal (July 1941, vol.2, is.4, p.398-409). http://journals.lww.com/anesthesiology/citation/1941/07000/Technical_Development_of_Gas_Anesthesia.4.aspx.
- ↑ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ "George Poe is Dead". Washington Post. February 3, 1914. http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/washingtonpost_historical/access/243050292.html?dids=243050292:243050292&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&date=FEB+03%2C+1914&author=&pub=The+Washington+Post&desc=GEORGE+POE+IS+DEAD&pqatl=google. Retrieved 2007-12-29. "Cousin of Famous Poet and Noted as a Scientist. Inventor of the Respirator. Also First to Liquefy Nitrous Oxide. Cadet at Virginia Military Institute at Time of Battle of Newmarket. Mentioned for the Nobel Prize for Scientific Attainment in Chemistry. Prof. George Poe, a cousin of the poet Edgar Allan Poe, a noted scientist and inventor, who had been mentioned for the Nobel prize for scientific attainment, a former resident of Washington, died in Norfolk, Virginia, yesterday of general paralysis. Prof. Poe was in his sixty-eighth year."
- ↑ "Nitrous oxide plant". Sanghi Organization. http://www.sanghioverseas.com/nitrous_oxide_gas_plants/nitrous_oxide_gas_plants.htm.
- ↑ Synthesis of Nitrous Oxide by Oxidation of Ammonia T Suwa, A Matsushima, Y Suziki, Y Namina, Kohyo Kagaku Zasshi, 1961; Showa Denka Ltd.
- ↑ Brozadzhiew & Rettos, 1975.
- ↑ Reimer R. A.; Slaten C. S.; Seapan M.; Lower M. W.; Tomlinson P. E.; (1994). "Abatement of N2O emissions produced in the adipic acid industry". Environmental progress 13 (2): 134–137. doi:10.1002/ep.670130217.
- ↑ .A. Shimizu, , K. Tanaka and M. Fujimori (2000). "Abatement of N2O emissions produced in the adipic acid industry". Chemosphere – Global Change Science 2 (3-4): 425–434. doi:10.1016/S1465-9972(00)00024-6.
- ↑ Nitrous Oxide Fuel Blend Monopropellants, Patentdocs, http://www.faqs.org/patents/app/20090133788, retrieved 2009-11-11
- ↑ FireStar Engineering, LLC, FireStar Engineering, http://www.firestar-engineering.com/, retrieved 2009-12-11
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Holley. "Holley performance products, FAQ for Nitrous Oxide Systems". http://www.holley.com/TechService/FAQ.asp?category=NOS.
- ↑ Dental Fear Central (2004). "Inhalation sedation (aka Laughing Gas)". http://www.dentalfearcentral.org/laughing_gas.html. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- ↑ AJ Giannini. Volatiles. In NS Miller (Ed.). Comprehensive Handbook of Drug and Alcohol Addiction. NY, Marcel Dekker, 1991 ISBN 082478474X
- ↑ Whalley MG, Brooks GB. (2009). Enhancement of suggestibility and imaginative ability with nitrous oxide. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 203(4):745-52. 10.1007/s00213-008-1424-0 PMID 19057896
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Yamakura T, Harris RA (2000). "Effects of gaseous anesthetics nitrous oxide and xenon on ligand-gated ion channels. Comparison with isoflurane and ethanol". Anesthesiology 93 (4): 1095–101. doi:10.1097/00000542-200010000-00034. PMID 11020766. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0003-3022&volume=93&issue=4&spage=1095.
- ↑ Mennerick S, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Todorovic SM, Shen W, Olney JW, Zorumski CF (1998). "Effect of nitrous oxide on excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in hippocampal cultures". The Journal of Neuroscience : the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience 18 (23): 9716–26. PMID 9822732.
- ↑ Gruss M, Bushell TJ, Bright DP, Lieb WR, Mathie A, Franks NP (2004). "Two-pore-domain K+ channels are a novel target for the anesthetic gases xenon, nitrous oxide, and cyclopropane". Molecular Pharmacology 65 (2): 443–52. doi:10.1124/mol.65.2.443. PMID 14742687.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Emmanouil DE, Quock RM (2007). [9:AIUTAO2.0.CO;2 "Advances in understanding the actions of nitrous oxide"]. Anesthesia Progress 54 (1): 9–18. doi:10.2344/0003-3006(2007)54[9:AIUTAO]2.0.CO;2. PMID 17352529. PMC 1821130. http://www.anesthesiaprogress.org/doi/abs/10.2344/0003-3006(2007)54[9:AIUTAO]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Emmanouil, D.E., Johnson, C.H. & Quock, R.M. (1994). "Nitrous oxide anxiolytic effect in mice in the elevated plus maze: mediation by benzodiazepine receptors". Psychopharmacology 115 (1-2): 167–72. doi:10.1007/BF02244768. PMID 7862891.
- ↑ Zacny, J.P., Yajnik, S., Coalson, D., Lichtor, J.L., Apfelbaum, J.L., Rupani, G., Young, C., Thapar, P. & Klafta, J. (1995). "Flumazenil may attenuate some subjective effects of nitrous oxide in humans: a preliminary report". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 51 (4): 815–9. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(95)00039-Y. PMID 7675863.
- ↑ Berkowitz, B.A., Finck, A.D., Hynes, M.D. & Ngai, S.H. (1979). "Tolerance to nitrous oxide analgesia in rats and mice". Anesthesiology 51 (51): 309–12. doi:10.1097/00000542-197910000-00006.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Branda, E.M., Ramza, J.T., Cahill, F.J., Tseng, L.F. & Quock, R.M. (2000). "Role of brain dynorphin in nitrous oxide antinociception in mice". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 65: 217–21. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(99)00202-6.
- ↑ Guo, T.Z., Davies, M.F., Kingery, W.S., Patterson, A.J., Limbird, L.E. & Maze, M. (1999). "Nitrous oxide produces antinociceptive response via alpha2B and/or alpha2C adrenoceptor subtypes in mice". Anesthesiology 90 (2): 470–6. doi:10.1097/00000542-199902000-00022. PMID 9952154. http://www.anesthesiology.org/pt/re/anes/abstract.00000542-199902000-00022.htm.
- ↑ Sawamura, S., Kingery, W.S., Davies, M.F., Agashe, G.S., Clark, J.D., Koblika, B.K., Hashimoto, T. & Maze, M. (2000). "Antinociceptive action of nitrous oxide is mediated by stimulation of noradrenergic neurons in the brainstem and activation of [alpha]2B adrenoceptors". J. Neurosci. 20 (24): 9242–51. PMID 11125002.
- ↑ Maze M, Fujinaga M (2000). "Recent advances in understanding the actions and toxicity of nitrous oxide". Anaesthesia 55 (4): 311–4. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2044.2000.01463.x. PMID 10781114.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Sakamoto S, Nakao S, Masuzawa M, et al. (2006). "The differential effects of nitrous oxide and xenon on extracellular dopamine levels in the rat nucleus accumbens: a microdialysis study". Anesthesia and Analgesia 103 (6): 1459–63. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000247792.03959.f1. PMID 17122223.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Benturquia N, Le Marec T, Scherrmann JM, Noble F (2008). "Effects of nitrous oxide on dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens and expectation of reward". Neuroscience 155 (2): 341–4. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.015. PMID 18571333.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 Lichtigfeld FJ, Gillman MA (1996). "Role of dopamine mesolimbic system in opioid action of psychotropic analgesic nitrous oxide in alcohol and drug withdrawal". Clinical Neuropharmacology 19 (3): 246–51. doi:10.1097/00002826-199619030-00006. PMID 8726543.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Koyanagi S, Himukashi S, Mukaida K, Shichino T, Fukuda K (2008). "Dopamine D2-like receptor in the nucleus accumbens is involved in the antinociceptive effect of nitrous oxide". Anesthesia and Analgesia 106 (6): 1904–9. doi:10.1213/ane.0b013e318172b15b. PMID 18499630.
- ↑ David HN, Ansseau M, Lemaire M, Abraini JH (2006). "Nitrous oxide and xenon prevent amphetamine-induced carrier-mediated dopamine release in a memantine-like fashion and protect against behavioral sensitization". Biological Psychiatry 60 (1): 49–57. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.10.007. PMID 16427030.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Benturquia N, Le Guen S, Canestrelli C, et al. (2007). "Specific blockade of morphine- and cocaine-induced reinforcing effects in conditioned place preference by nitrous oxide in mice". Neuroscience 149 (3): 477–86. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.08.003. PMID 17905521.
- ↑ Ramsay DS, Watson CH, Leroux BG, Prall CW, Kaiyala KJ (2003). "Conditioned place aversion and self-administration of nitrous oxide in rats". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 74 (3): 623–33. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(02)01048-1. PMID 12543228.
- ↑ Wood RW, Grubman J, Weiss B (1977). "Nitrous oxide self-administration by the squirrel monkey". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 202 (3): 491–9. PMID 408480.
- ↑ Zacny JP, Galinkin JL (1999). "Psychotropic drugs used in anesthesia practice: abuse liability and epidemiology of abuse". Anesthesiology 90 (1): 269–88. PMID 9915336. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0003-3022&volume=90&issue=1&spage=269.
- ↑ Dohrn CS, Lichtor JL, Coalson DW, Uitvlugt A, de Wit H, Zacny JP (1993). "Reinforcing effects of extended inhalation of nitrous oxide in humans". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 31 (3): 265–80. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(93)90009-F. PMID 8462415.
- ↑ Walker DJ, Zacny JP (2001). "Within- and between-subject variability in the reinforcing and subjective effects of nitrous oxide in healthy volunteers". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 64 (1): 85–96. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(00)00234-9. PMID 11470344.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Beals J, Benshoff N, Olney JW (2003). "Prolonged exposure to inhalational anesthetic nitrous oxide kills neurons in adult rat brain". Neuroscience 122 (3): 609–16. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.07.012. PMID 14622904.
- ↑ Nakao S, Nagata A, Masuzawa M, et al. (2003). "[NMDA receptor antagonist neurotoxicity and psychotomimetic activity]" (in Japanese). Masui. the Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 52 (6): 594–602. PMID 12854473.
- ↑ Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Benshoff N, Olney JW (2000). "Ketamine potentiates cerebrocortical damage induced by the common anaesthetic agent nitrous oxide in adult rats". British Journal of Pharmacology 130 (7): 1692–8. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703479. PMID 10928976.
- ↑ Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Carter LB (2005). "The anesthetics nitrous oxide and ketamine are more neurotoxic to old than to young rat brain". Neurobiology of Aging 26 (6): 947–56. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.07.009. PMID 15718054.
- ↑ Abraini JH, David HN, Lemaire M (2005). "Potentially neuroprotective and therapeutic properties of nitrous oxide and xenon". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1053: 289–300. doi:10.1196/annals.1344.025. PMID 16179534.
- ↑ Criteria for a recommended standard: occupational exposure to waste anesthetic gases and vapors. Cincinnati, OH: U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Center for Disease Control, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, DHEW (NIOSH) Publication No. 77B140.
- ↑ CDC.gov NIOSH Alert: Controlling Exposures to Nitrous Oxide During Anesthetic Administration. Cincinnati, OH: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 94-100
- ↑ Air Liquid data on Nitrous oxide
- ↑ Vaseline triggered explosion of hybrid rocket
- ↑ Safetygram 20: Nitrous Oxide
- ↑ Nitrous Oxide Trailer Rupture July 2, 2001 Report at CGA Seminar “Safety and Reliability of Industrial Gases, Equipment and Facilities”, October 15–17, 2001, St. Louis, Missouri by Konrad Munke, LindeGas AG
- ↑ AJ Giannini. Drug Abuse. Los Angeles, Health Information Press, 1999 ISBN 1885987110
- ↑ Rowland, AS; Baird, DD; Weinberg, CR; Shore, DL; Shy, CM; Wilcox, AJ (1992). "Reduced fertility among women employed as dental assistants exposed to high levels of nitrous oxide.". The New England journal of medicine 327 (14): 993–7. PMID 1298226.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 Vieira, E; Cleaton-Jones, P; Austin, JC; Moyes, DG; Shaw, R (1980). "Effects of low concentrations of nitrous oxide on rat fetuses.". Anesthesia and analgesia 59 (3): 175–7. PMID 7189346.
- ↑ Vieira, E (1979). "Effect of the chronic administration of nitrous oxide 0.5% to gravid rats.". British journal of anaesthesia 51 (4): 283–7. doi:10.1093/bja/51.4.283. PMID 465253.
- ↑ Vieira, E; Cleaton-Jones, P; Moyes, D (1983). "Effects of low intermittent concentrations of nitrous oxide on the developing rat fetus.". British journal of anaesthesia 55 (1): 67–9. doi:10.1093/bja/55.1.67. PMID 6821624.
- ↑ Manure, HD TVs Among Greenhouse Gas Sources to Watch John Roach National Geographic News September 8, 2009
- ↑ "Sources and Emissions -- Where Does Nitrous Oxide Come From?". U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2006. http://www.epa.gov/nitrousoxide/sources.html. Retrieved 2008-02-02.
- ↑ "N2O release from agro-biofuel production negates global warming reduction by replacing fossil fuels". http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/8/389.
- ↑ "Climate Change 2007: The Physical Sciences Basis". IPCC. http://ipcc-wg1.ucar.edu/wg1/wg1-report.html. Retrieved 2007-04-30.
- ↑ Sciencemag.org
- ↑ Newscientist.com
- ↑ Center for Cognitive Liberty and Ethics: State Laws Concerning Inhalation of Nitrous Oxide
- ↑ CAL. PEN. CODE § 381b : California Code – Section 381b
- ↑ Beehive.govt.nz – Time's up for sham sales of laughing gas
External links
- Occupational Safety and Health Guideline for Nitrous Oxide
- Paul Crutzen Interview Freeview video of Paul Crutzen Nobel Laureate for his work on decomposition of ozone talking to Harry Kroto Nobel Laureate by the Vega Science Trust.
- National Pollutant Inventory – Oxide of nitrogen fact sheet
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health – Nitrous Oxide
- Nitrous Oxide FAQ
- Erowid article on Nitrous Oxide
- Nitrous oxide fingered as monster ozone slayer, Science News
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||
